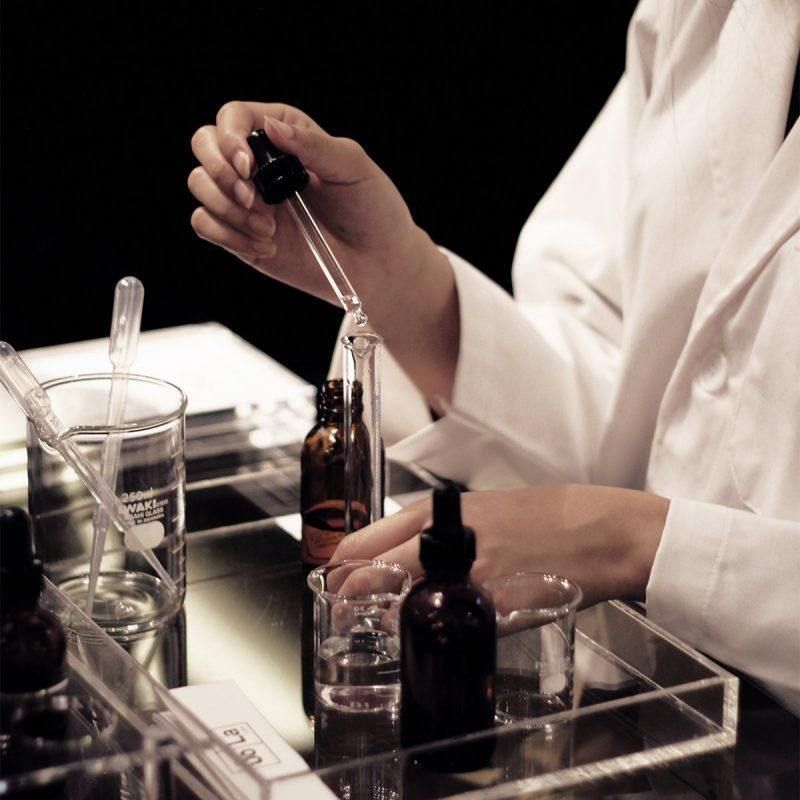
Coumarin, for Tonka bean note
Coumarin, for Tonka bean note
Coumarin, occurs naturally in tonka beans and cinnamon, but can also be found in trace amounts in bison grass, green tea, carrots, and even some beers.
Coumarin may be described as a sweet, aromatic, creamy vanilla bean odour with nut-like tones that are heavy, but not sharp or brilliant. Coumarin has a burning, bitter taste when concentrated, but this effect fades to a sweet herbaceous impression when coumarin is diluted. It blends well and does not stand out.
Coumarin is a fragrance material with a very sweet, vanilla-like aroma, which is often described as similar to new-mown hay. It may also be described as spicy and slightly tobacco like.
Coumarin is a chemical compound, occurring naturally in some essential oils and absolutes, such as cinnamon, lavender, tonka, lemongrass, rose, tagetes, and tarragon.
-------------------------------------------------
The Aroma Chemical Brothers
Hedione, for blooming floralcy
Bacdanol for creamy sandalwood note
Iso E Super for long-lasting woody note
Dihydromyrcenol for citrus and green tea
Helional for aquatic, ozone note
Galaxolide for clean white musk
Benzyl salicylate for Orchid note
Beta Pinene for forest fresh effect
Buccoxime for blackcurrant juicy effect
-------------------------------------------------